

Polyphenols in the Protection Against Cardiovascular Disease and Dementia
In a recently published study—NutriNet-Santé (10/2018)—that included the analysis of dietary records of 84,158 French adults that spanned between May 2009 and June 20017— the study authors concluded found that “Higher intakes of polyphenols, especially anthocyanins and catechins (flavan-3-ols), were associated with a statistically significant decreased cardiovascular disease risk.”(1).
The polyphenol intake was primarily derived from coffee (49%), tea (23%), fruits (17%), vegetables (8%), and wine (5%). (more…)

MEMBER ACCESS: Mercury Depletes Glutathione Peroxidase-Toxic Mechanisms In Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
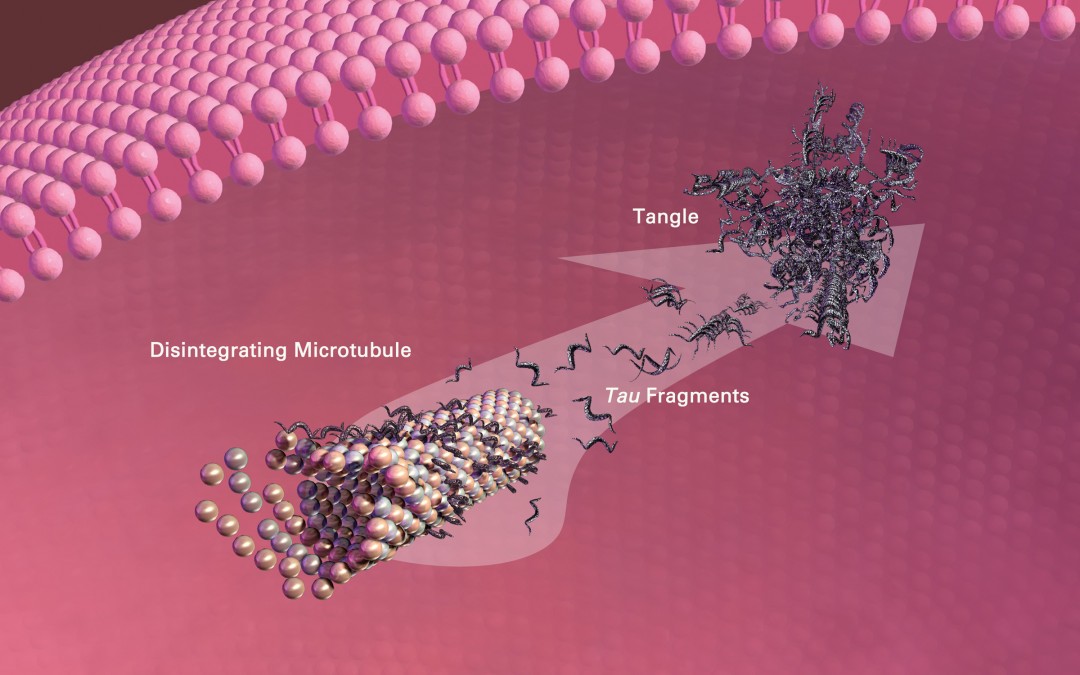
MEMBER ACCESS: Oxidative Stress and the Thromboxane Receptor—A Central Pivot in the Production of Neurofibrillary Tangles

MEMBER ACCESS: Blueberry Polyphenols Protect the Brain from the Degenerative Processes Associated with Brain Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease






